Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Docker deploy MySQL cluster
- 3 Via My Youtube
- 4 Conclusion
Introduction
In this tutorial, How to use Docker deploy MySQL cluster and connect to the nodes from your local machine. We will be deploying the MySQL server with docker.
To deploy a MySQL cluster using Docker, you can use the MySQL official Docker images and Docker Compose. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- 1 Management node
- 2 Data nodes
- 2 SQL nodes
The nodes in the cluster are running on separate hosts in a network.
First, You have installed docker on your machine.
Docker deploy MySQL cluster
Step 1: Create the docker network.
I will create a network for MySQL cluster with the following docker command.
docker network create cluster --subnet=192.168.4.0/24Step 2: Get the mysql docker repository
git clone https://github.com/mysql/mysql-docker.git
cd mysql-docker
git checkout -b mysql-clusterI will change the IP address of each node to match the subnet. Open mysql-cluster/8.0/cnf/mysql-cluster.cnf file
For example
[ndbd default]
NoOfReplicas=2
DataMemory=80M
IndexMemory=18M
[ndb_mgmd]
NodeId=1
hostname=192.168.4.2
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
[ndbd]
NodeId=2
hostname=192.168.4.3
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
[ndbd]
NodeId=3
hostname=192.168.4.4
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
[mysqld]
NodeId=4
hostname=192.168.4.10
[mysqld]
NodeId=5
hostname=192.168.4.11Open mysql-cluster/8.0/cnf/my.cnf and modify as below
[mysqld]
ndbcluster
ndb-connectstring=192.168.4.2
user=mysql
[mysql_cluster]
ndb-connectstring=192.168.4.2Docker image build
docker build -t <image_name> <Path to docker file>
docker build -t mysql-cluster mysql-cluster/8.0Step 3: Create the manager node.
docker run -d --net=cluster --name=management1 --ip=192.168.4.2 mysql-cluster ndb_mgmdStep 4: Create the data nodes
docker run -d --net=cluster --name=ndb1 --ip=192.168.4.3 mysql-cluster ndbd
docker run -d --net=cluster --name=ndb2 --ip=192.168.4.4 mysql-cluster ndbd
Step 5: Create the SQL nodes.
docker run -d --net=cluster --name=mysql1 --ip=192.168.4.10 -e MYSQL_RANDOM_ROOT_PASSWORD=true mysql-cluster mysqld
docker run -d --net=cluster --name=mysql2 --ip=192.168.4.11 -e MYSQL_RANDOM_ROOT_PASSWORD=true mysql-cluster mysqld
docker run -it --net=cluster mysql-cluster ndb_mgmThe cluster management console will be loaded.
[Entrypoint] MySQL Docker Image 8.0.28-1.2.7-cluster
[Entrypoint] Starting ndb_mgm
-- NDB Cluster -- Management Client --
ndb_mgm>Run show command
ndb_mgm> show
Connected to Management Server at: 192.168.4.2:1186
Cluster Configuration
---------------------
[ndbd(NDB)] 2 node(s)
id=2 @192.168.4.3 (mysql-8.0.28 ndb-8.0.28, Nodegroup: 0, *)
id=3 @192.168.4.4 (mysql-8.0.28 ndb-8.0.28, Nodegroup: 0)
[ndb_mgmd(MGM)] 1 node(s)
id=1 @192.168.4.2 (mysql-8.0.28 ndb-8.0.28)
[mysqld(API)] 2 node(s)
id=4 @192.168.4.10 (mysql-8.0.28 ndb-8.0.28)
id=5 @192.168.4.11 (mysql-8.0.28 ndb-8.0.28)
ndb_mgm>Step 7. Change the default passwords.
MySQL node 1:
The SQL nodes are created initially, with a random password. Get the default password.
docker logs mysql1 2>&1 | grep PASSWORD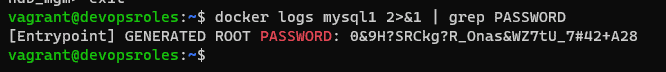
To change the password, first, Input the password default at Step 7
docker exec -it mysql1 mysql -uroot -p
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;MySQL node 2:
The SQL nodes are created initially, with a random password. Get the default password.
docker logs mysql2 2>&1 | grep PASSWORD
To change the password, first, Input the password default at Step 7
docker exec -it mysql2 mysql -uroot -p
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Step 8: Login and create a new database.
For example, I will create huupv an account on mysql1 and mysql2 containers and access any hosts.
# For mysql1
docker exec -it mysql1 mysql -uroot -p
CREATE USER 'huupv'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456789';
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'huupv'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
# For mysql2
docker exec -it mysql2 mysql -uroot -p
CREATE USER 'huupv'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456789';
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'huupv'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Create new a database.
create schema test_db;The output terminal is as below:
vagrant@devopsroles:~/mysql-docker$ docker exec -it mysql1 mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 15
Server version: 8.0.28-cluster MySQL Cluster Community Server - GPL
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE USER 'huupv'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456789';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'huupv'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
vagrant@devopsroles:~/mysql-docker$ docker exec -it mysql2 mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 16
Server version: 8.0.28-cluster MySQL Cluster Community Server - GPL
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE USER 'huupv'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456789';
ERROR 1396 (HY000): Operation CREATE USER failed for 'huupv'@'%'
mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'huupv'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
vagrant@devopsroles:~/mysql-docker$Login from my machine.
mysql -h192.168.4.10 -uhuupv -p
mysql -h192.168.4.11 -uhuupv -pVia My Youtube
Conclusion
You have successfully deployed a MySQL cluster using Docker. You can now use the cluster for your applications or explore additional configuration options for MySQL clustering, such as replication and high availability. I hope will this your helpful. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

Hi there, thanks for your blog, it really helps me a lot.
I got some errors while i follow your tutorial to setup a cluster. when i run the code “docker build -t mysql-cluster mysql-cluster/8.0” error occured like:
> [2/9] RUN rpm -U http://repo.mysql.oraclecorp.com/mysql-uat/repos-stage/mysql-cluster-community-minimal-release-el8.rpm && rpm -U http://repo.mysql.oraclecorp.com/mysql-uat/repos-stage/mysql80-community-release-el8.rpm:
#5 8.474 curl: (6) Could not resolve host: repo.mysql.oraclecorp.com
#5 8.474 error: skipping http://repo.mysql.oraclecorp.com/mysql-uat/repos-stage/mysql-cluster-community-minimal-release-el8.rpm – transfer failed
——
executor failed running [/bin/sh -c rpm -U http://repo.mysql.oraclecorp.com/mysql-uat/repos-stage/mysql-cluster-community-minimal-release-el8.rpm && rpm -U http://repo.mysql.oraclecorp.com/mysql-uat/repos-stage/mysql80-community-release-el8.rpm%5D: exit code: 1
and a search the original git repo and find nothing.
can you give me some advices?
Change the repo address in Dockerfiles to the following:
RUN rpm -U http://repo.mysql.com/mysql-cluster-community-minimal-release-el8.rpm \
&& rpm -U http://repo.mysql.com/mysql80-community-release-el8.rpm
But how we can connect from mysql workbench
Hi Ganesh
To connect to your MySQL cluster deployed with Docker from MySQL Workbench, follow these simple steps:
1. Check Your Container Information
First, you need to check the details of your running MySQL container. Use the following command to list all running containers:
bash
Copy code
docker ps
Find your MySQL container and note the CONTAINER ID and the PORT MySQL is listening on.
2. Connect Using MySQL Workbench
Open MySQL Workbench: Start MySQL Workbench on your computer.
Create a New Connection:
Click the + button to create a new connection.
Fill in the required information:
Connection Name: Give your connection a name.
Hostname: The IP address of your Docker host or localhost if you’re connecting from the same machine.
Port: The port MySQL container is listening on (e.g., 3306).
Username: Your MySQL username (e.g., root).
Password: The password for your MySQL user.
Test the Connection:
Click Test Connection to check if the connection works. If everything is set up correctly, you should see a success message.
3. Additional Notes
Docker Network: If your MySQL container is running on a custom Docker network, ensure your machine can access that network. You might need to specify the network when running your container.
Port: Make sure the MySQL port (e.g., 3306) is open and not blocked by a firewall.
Example Docker Command
If you started your MySQL container with the following command:
bash
Copy code
docker run –name mysql-container -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -p 3306:3306 -d mysql:latest
You can connect from MySQL Workbench using these details:
Hostname: localhost
Port: 3306
Username: root
Password: my-secret-pw
I hope this helps you connect MySQL Workbench to your MySQL cluster deployed with Docker successfully!