Scaling your AWS environment efficiently and securely is crucial for any organization, regardless of size. Manual scaling processes are prone to errors, inconsistencies, and security vulnerabilities. This leads to increased operational costs, downtime, and potential security breaches. This comprehensive guide will demonstrate how to effectively scale AWS environment securely using Terraform for infrastructure-as-code (IaC) and Sentinel for policy-as-code, creating a robust and repeatable process. We’ll explore best practices and practical examples to ensure your AWS infrastructure remains scalable, resilient, and secure throughout its lifecycle.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Challenges of Scaling AWS
Scaling AWS infrastructure presents several challenges. Manually managing resources, configurations, and security across different environments (development, testing, production) is tedious and error-prone. Inconsistent configurations lead to security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and operational inefficiencies. As your infrastructure grows, managing this complexity becomes exponentially harder, leading to increased costs and risks. Furthermore, ensuring consistent security policies across your expanding infrastructure requires significant effort and expertise.
- Manual Configuration Errors: Human error is inevitable when managing resources manually. Mistakes in configuration can lead to security breaches or operational failures.
- Inconsistent Environments: Differences between environments (dev, test, prod) can cause deployment issues and complicate debugging.
- Security Gaps: Manual security management can lead to inconsistencies and oversight, leaving your infrastructure vulnerable.
- Scalability Limitations: Manual processes struggle to keep pace with the dynamic demands of a growing application.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Terraform
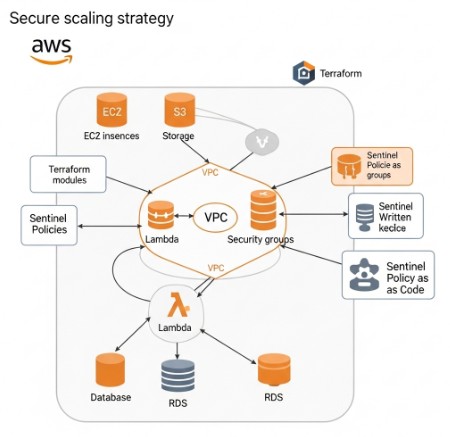
Terraform addresses these challenges by enabling you to define and manage your infrastructure as code. This means representing your AWS resources (EC2 instances, S3 buckets, VPCs, etc.) in declarative configuration files. Terraform then automatically provisions and manages these resources based on your configurations. This eliminates manual processes, reduces errors, and improves consistency.
Terraform Basics
Terraform uses the HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) to define infrastructure. A simple example of creating an EC2 instance:
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-0c55b31ad2299a701" # Replace with your AMI ID
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
Scaling with Terraform
Terraform allows for easy scaling through variables and modules. You can define variables for the number of instances, instance type, and other parameters. This enables you to easily adjust your infrastructure’s scale by modifying these variables. Modules help organize your code into reusable components, making scaling more efficient and manageable.
Policy as Code with Sentinel
While Terraform handles infrastructure provisioning, Sentinel ensures your infrastructure adheres to your organization’s security policies. Sentinel allows you to define policies in a declarative way, which are then evaluated by Terraform before deploying changes. This prevents deployments that violate your security rules, reinforcing a secure scale AWS environment securely strategy.
Sentinel Policies
Sentinel policies are written in a dedicated language designed for policy enforcement. An example of a policy that checks for the minimum required instance type:
policy "instance_type_check" {
rule "minimum_instance_type" {
when aws_instance.example.instance_type != "t2.medium" {
message = "Instance type must be at least t2.medium"
}
}
}
Integrating Sentinel with Terraform
Integrating Sentinel with Terraform involves configuring the Sentinel provider and defining the policies that need to be enforced. Terraform will then automatically evaluate these policies before applying any infrastructure changes. This ensures that only configurations that meet your security requirements are deployed.
Scale AWS Environment Securely: Best Practices
Implementing a secure and scalable AWS environment requires adhering to best practices:
- Version Control: Store your Terraform and Sentinel code in a version control system (e.g., Git) for tracking changes and collaboration.
- Modular Design: Break down your infrastructure into reusable modules for better organization and scalability.
- Automated Testing: Implement automated tests to validate your infrastructure code and policies.
- Security Scanning: Use security scanning tools to identify potential vulnerabilities in your infrastructure.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to restrict access to your AWS resources based on roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Audits: Regularly review and update your security policies to reflect changing threats and vulnerabilities.
Advanced Techniques
For more advanced scenarios, consider these techniques:
- Terraform Cloud/Enterprise: Manage your Terraform state and collaborate efficiently using Terraform Cloud or Enterprise.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Automate your infrastructure deployment process with a CI/CD pipeline.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) security scanning tools: Integrate static and dynamic code analysis tools within your CI/CD pipeline to catch security issues early in the development lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What if a Sentinel policy fails?
If a Sentinel policy fails, Terraform will prevent the deployment from proceeding. You will need to address the policy violation before the deployment can continue. This ensures that only compliant infrastructure is deployed.
2. Can I use Sentinel with other cloud providers?
While Sentinel is primarily used with Terraform, its core concepts are applicable to other IaC tools and cloud providers. The specific implementation details would vary depending on the chosen tools and platforms. The core principle of defining and enforcing policies as code remains constant.
3. How do I handle complex security requirements?
Complex security requirements can be managed by decomposing them into smaller, manageable policies. These policies can then be organized and prioritized within your Sentinel configuration. This promotes modularity, clarity, and maintainability.
4. What are the benefits of using Terraform and Sentinel together?
Using Terraform and Sentinel together provides a comprehensive approach to managing and securing your AWS infrastructure. Terraform automates infrastructure provisioning, ensuring consistency, while Sentinel enforces security policies, preventing configurations that violate your organization’s security standards. This helps in building a robust and secure scale AWS environment securely.
Conclusion
Scaling your AWS environment securely is paramount for maintaining operational efficiency and mitigating security risks. By leveraging the power of Terraform for infrastructure as code and Sentinel for policy as code, you can create a robust, scalable, and secure AWS infrastructure. Remember to adopt best practices such as version control, automated testing, and regular security audits to maintain the integrity and security of your environment. Employing these techniques allows you to effectively scale AWS environment securely, ensuring your infrastructure remains resilient and protected throughout its lifecycle. Remember to consistently review and update your policies to adapt to evolving security threats and best practices.
For further reading, refer to the official Terraform documentation: https://www.terraform.io/ and the Sentinel documentation: https://www.hashicorp.com/products/sentinel. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

