Managing Oracle databases in the cloud can be complex. Choosing the right solution to balance performance, cost, and control is crucial. This guide delves into leveraging Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle and Terraform to automate the deployment and management of your Oracle databases, offering a more tailored and efficient solution than standard RDS offerings. We’ll walk you through the process, from initial configuration to advanced customization, addressing potential challenges and best practices along the way. This comprehensive tutorial will equip you with the knowledge to successfully deploy and manage your Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle instances using Terraform’s infrastructure-as-code capabilities.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
- 2 Deploying Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle with Terraform
- 3 Managing Your Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle Instance
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 4.1 Q1: What are the key differences between Amazon RDS for Oracle and Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle?
- 4.2 Q2: How do I handle patching and maintenance with Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle?
- 4.3 Q3: What are the cost implications of using Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle?
- 4.4 Q4: Can I use Terraform to manage backups for my Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle instance?
- 5 Conclusion
Understanding Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
Unlike standard Amazon RDS for Oracle, which offers predefined instance types and configurations, Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle provides granular control over the underlying EC2 instance. This allows you to choose specific instance types, optimize your storage, and fine-tune your networking parameters for optimal performance and cost efficiency. This increased control is particularly beneficial for applications with demanding performance requirements or specific hardware needs that aren’t met by standard RDS offerings. However, this flexibility requires a deeper understanding of Oracle database administration and infrastructure management.
Key Benefits of Using Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
- Granular Control: Customize your instance type, storage, and networking settings.
- Cost Optimization: Choose instance types tailored to your workload, reducing unnecessary spending.
- Performance Tuning: Fine-tune your database environment for optimal performance.
- Enhanced Security: Benefit from the security features inherent in AWS.
- Automation: Integrate with tools like Terraform for automated deployments and management.
Limitations of Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle
- Increased Complexity: Requires a higher level of technical expertise in Oracle and AWS.
- Manual Patching: You’re responsible for managing and applying patches.
- Higher Operational Overhead: More manual intervention might be required for maintenance and troubleshooting.
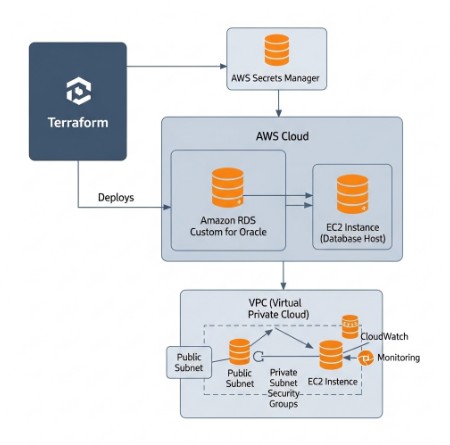
Deploying Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle with Terraform
Terraform provides a robust and efficient way to manage infrastructure-as-code. Using Terraform, we can automate the entire deployment process for Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle, ensuring consistency and repeatability. Below is a basic example showcasing the core components of a Terraform configuration for Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle. Remember to replace placeholders with your actual values.
Setting up the Terraform Environment
- Install Terraform: Download and install the appropriate version of Terraform for your operating system from the official website. https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
- Configure AWS Credentials: Configure your AWS credentials using the AWS CLI or environment variables. Ensure you have the necessary permissions to create and manage RDS instances.
- Create a Terraform Configuration File (main.tf):
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1" # Replace with your desired region
}
resource "aws_rds_cluster" "example" {
cluster_identifier = "my-oracle-custom-cluster"
engine = "oracle-ee"
engine_version = "19.0" # Replace with your desired version
master_username = "admin"
master_password = "password123" # Ensure you use a strong password!
# ... other configurations ...
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.default.name
# RDS Custom configurations
custom_engine_version = "19.0" # This should match the engine_version
custom_iam_role_name = aws_iam_role.rds_custom_role.name
}
resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "default" {
name = "my-oracle-custom-subnet-group"
subnet_ids = ["subnet-xxxxxxxx", "subnet-yyyyyyyy"] # Replace with your subnet IDs
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "rds_custom_role" {
name = "rds-custom-role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "rds.amazonaws.com"
}
}
]
})
}Implementing Advanced Configurations
The above example provides a basic setup. For more advanced configurations, consider the following:
- High Availability (HA): Configure multiple Availability Zones for redundancy.
- Read Replicas: Implement read replicas to improve scalability and performance.
- Automated Backups: Configure automated backups using AWS Backup.
- Security Groups: Define specific inbound and outbound rules for your RDS instances.
- Monitoring: Integrate with AWS CloudWatch to monitor the performance and health of your database.
Managing Your Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle Instance
After deployment, regular maintenance and monitoring are vital. Remember to regularly apply security patches and monitor resource utilization. Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle requires more proactive management than standard RDS due to the increased level of control and responsibility. Proper monitoring and proactive maintenance are crucial to ensure high availability and optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the key differences between Amazon RDS for Oracle and Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle?
Amazon RDS for Oracle offers pre-configured instance types and managed services, simplifying management but limiting customization. Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle provides granular control over the underlying EC2 instance, enabling custom configurations for specific needs but increasing management complexity. The choice depends on the balance required between ease of management and the level of customization needed.
Q2: How do I handle patching and maintenance with Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle?
Unlike standard RDS, which handles patching automatically, Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle requires you to manage patches manually. This involves regular updates of the Oracle database software, applying security patches, and performing necessary maintenance tasks. This requires a deeper understanding of Oracle database administration.
Q3: What are the cost implications of using Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle?
The cost of Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle can vary depending on the chosen instance type, storage, and other configurations. While it allows for optimization, careful planning and monitoring are needed to avoid unexpected costs. Use the AWS Pricing Calculator to estimate the costs based on your chosen configuration. https://calculator.aws/
Q4: Can I use Terraform to manage backups for my Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle instance?
Yes, you can integrate Terraform with AWS Backup to automate the backup and restore processes for your Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle instance. This allows for consistent and reliable backup management, crucial for data protection and disaster recovery.
Conclusion
Deploying Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle with Terraform provides a powerful and flexible approach to managing your Oracle databases in the AWS cloud. While it requires a deeper understanding of both Oracle and AWS, the level of control and optimization it offers is invaluable for demanding applications. By following the best practices outlined in this guide and understanding the nuances of Amazon RDS Custom for Oracle, you can effectively leverage this service to create a robust, scalable, and cost-effective database solution. Remember to thoroughly test your configurations in a non-production environment before deploying to production. Proper planning and a thorough understanding of the service are crucial for success. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

