Managing infrastructure across diverse environments can be a daunting task, often involving complex configurations and repetitive manual processes. This complexity increases exponentially as your infrastructure scales. This is where AWS Systems Manager Ansible comes into play, offering a powerful solution for automating infrastructure management and configuration tasks across your AWS ecosystem and beyond. This comprehensive guide will explore the seamless integration of Ansible with AWS Systems Manager, detailing its benefits, implementation strategies, and best practices. We will delve into how this powerful combination simplifies your workflows and improves operational efficiency, leading to effortless management of your entire infrastructure.
Table of Contents
- 1 Understanding the Power of AWS Systems Manager and Ansible
- 2 Setting Up AWS Systems Manager Ansible
- 3 Implementing AWS Systems Manager Ansible: Practical Examples
- 4 Advanced Techniques with AWS Systems Manager Ansible
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 5.1 Q1: What are the security considerations when using AWS Systems Manager Ansible?
- 5.2 Q2: How do I handle errors and exceptions in my AWS Systems Manager Ansible playbooks?
- 5.3 Q3: Can I use AWS Systems Manager Ansible to manage on-premises infrastructure?
- 5.4 Q4: What are the costs associated with using AWS Systems Manager Ansible?
- 6 Conclusion
Understanding the Power of AWS Systems Manager and Ansible
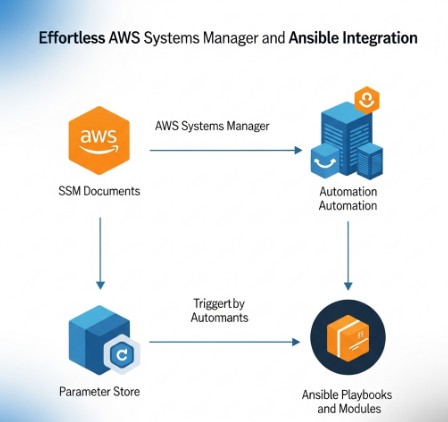
AWS Systems Manager (SSM) is a comprehensive automation and management service that allows you to automate operational tasks, manage configurations, and monitor your AWS resources. On the other hand, Ansible is a popular open-source automation tool known for its agentless architecture and simple, human-readable YAML configuration files. Combining these two powerful tools creates a synergistic effect, drastically improving the ease and efficiency of IT operations.
Why Integrate AWS Systems Manager with Ansible?
- Centralized Management: Manage both your AWS-native and on-premises infrastructure from a single pane of glass using SSM as a central control point.
- Simplified Automation: Leverage Ansible’s straightforward syntax to create reusable and easily maintainable automation playbooks for various tasks.
- Agentless Architecture: Ansible’s agentless approach simplifies deployment and maintenance, reducing operational overhead.
- Improved Security: Securely manage your credentials and access keys using SSM Parameter Store, enhancing your overall security posture.
- Scalability and Reliability: Scale your automation efforts easily as your infrastructure grows, benefiting from the robustness and scalability of both SSM and Ansible.
Setting Up AWS Systems Manager Ansible
Before diving into practical examples, let’s outline the prerequisites and steps to set up AWS Systems Manager Ansible. This involves configuring SSM, installing Ansible, and establishing the necessary connections.
Prerequisites
- An active AWS account.
- An AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user with appropriate permissions to access SSM and other relevant AWS services.
- Ansible installed on a management machine (this can be an EC2 instance or your local machine).
Step-by-Step Setup
- Configure IAM Roles: Create an IAM role that grants the necessary permissions to Ansible to interact with your AWS resources. This role needs permissions to access SSM, EC2, and any other services your Ansible playbooks will interact with.
- Install the AWS Systems Manager Ansible module: Use pip to install the necessary AWS Ansible modules:
pip install awscli boto3 ansible - Configure AWS Credentials: Set up your AWS credentials either through environment variables (AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, AWS_SESSION_TOKEN), an AWS credentials file (~/.aws/credentials), or through an IAM role assigned to the EC2 instance running Ansible.
- Test the Connection: Use the
aws sts get-caller-identitycommand to verify that your AWS credentials are properly configured. This confirms your Ansible instance can authenticate with AWS.
Implementing AWS Systems Manager Ansible: Practical Examples
Now, let’s illustrate the practical application of AWS Systems Manager Ansible with a few real-world examples. We’ll start with a basic example and gradually increase the complexity.
Example 1: Managing EC2 Instances
This example demonstrates how to start and stop an EC2 instance using Ansible and SSM.
---
- hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Start EC2 Instance
aws_ec2:
state: started
instance_ids:
- i-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx # Replace with your EC2 instance ID
- name: Wait for instance to be running
wait_for_connection:
delay: 10
timeout: 600
Example 2: Deploying Applications
Deploying and configuring applications across multiple EC2 instances using Ansible becomes significantly streamlined with AWS Systems Manager. You can leverage SSM Parameter Store to securely manage sensitive configuration data.
---
- hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Copy application files
copy:
src: /path/to/application
dest: /opt/myapp
- name: Set application configuration from SSM Parameter Store
ini_file:
path: /opt/myapp/config.ini
section: app
option: database_password
value: "{{ lookup('aws_ssm', 'path/to/database_password') }}"
Example 3: Patching EC2 Instances
Maintaining up-to-date software on your EC2 instances is critical for security. Ansible and SSM can automate the patching process, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and maintaining compliance.
---
- hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install updates
yum:
name: "*"
state: latest
when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'yum'
Advanced Techniques with AWS Systems Manager Ansible
Beyond basic operations, AWS Systems Manager Ansible enables advanced capabilities, including inventory management, automation using AWS Lambda, and integration with other AWS services.
Leveraging SSM Inventory
SSM Inventory provides a central repository for managing your infrastructure’s configuration and status. You can use this inventory within your Ansible playbooks to target specific instances based on various criteria (e.g., tags, operating system).
Integrating with AWS Lambda
Automate tasks triggered by events (e.g., new EC2 instance launch) by integrating Ansible playbooks with AWS Lambda. This creates a reactive automation system that responds dynamically to changes in your infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the security considerations when using AWS Systems Manager Ansible?
Security is paramount. Always use IAM roles to control access and avoid hardcoding credentials in your playbooks. Leverage SSM Parameter Store for securely managing sensitive data like passwords and API keys. Regularly review and update IAM policies to maintain a secure configuration.
Q2: How do I handle errors and exceptions in my AWS Systems Manager Ansible playbooks?
Ansible provides robust error handling mechanisms. Use handlers to perform actions only if errors occur. Implement proper logging to track errors and debug issues. Consider using Ansible’s retry mechanisms to handle transient network errors.
Q3: Can I use AWS Systems Manager Ansible to manage on-premises infrastructure?
While primarily designed for AWS, Ansible’s flexibility allows managing on-premises resources alongside your AWS infrastructure. You would need to configure Ansible to connect to your on-premises servers using appropriate methods like SSH and manage credentials securely.
Q4: What are the costs associated with using AWS Systems Manager Ansible?
Costs depend on your usage of the underlying AWS services (SSM, EC2, etc.). Ansible itself is open-source and free to use. Refer to the AWS Pricing page for detailed cost information on each service you utilize.
Conclusion
Integrating Ansible with AWS Systems Manager provides a powerful and efficient method for automating and managing your entire infrastructure. By leveraging the strengths of both tools, you can significantly simplify complex tasks, improve operational efficiency, and reduce manual intervention. Mastering AWS Systems Manager Ansible will undoubtedly enhance your DevOps capabilities, enabling you to confidently manage even the most complex and scalable cloud environments. Remember to prioritize security best practices throughout your implementation to safeguard your sensitive data and infrastructure.
For further information, refer to the official Ansible documentation here and the AWS Systems Manager documentation here. Also, exploring community resources and tutorials on using Ansible with AWS will prove invaluable. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

