Efficiently managing Python package dependencies is crucial for any organization relying on Python for software development. Slow or unreliable access to the Python Package Index (PyPI) can significantly hinder development speed and productivity. This article demonstrates how to establish a highly available and performant PyPI mirror within AWS using Terraform, enabling faster package resolution and improved resilience for your development workflows. We will cover the entire process, from infrastructure provisioning to configuration and maintenance, ensuring you have a robust solution for your Python dependency management.
Table of Contents
Planning Your PyPI Mirror Infrastructure
Before diving into the Terraform code, carefully consider these aspects of your PyPI mirror deployment:
- Region Selection: Choose an AWS region strategically positioned to minimize latency for your developers. Consider regions with robust network connectivity.
- Instance Size: Select an EC2 instance size appropriate for your anticipated package download volume. Start with a smaller instance type and scale up as needed.
- Storage: Determine the storage requirements based on the size of the packages you intend to mirror. Amazon EBS volumes are suitable; consider using a RAID configuration for improved redundancy and performance. For very large repositories, consider Amazon S3.
- High Availability: Implement a strategy for high availability. This usually involves at least two EC2 instances, load balancing, and potentially an auto-scaling group.
Setting up the AWS Infrastructure with Terraform
Terraform allows for infrastructure as code (IaC), enabling reproducible and manageable deployments. The following code snippets illustrate a basic setup. Remember to replace placeholders like
Creating the EC2 Instance
resource "aws_instance" "pypi_mirror" {
ami = ""
instance_type = "t3.medium"
key_name = ""
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.pypi_mirror.id]
tags = {
Name = "pypi-mirror"
}
}
Defining the Security Group
resource "aws_security_group" "pypi_mirror" {
name = "pypi-mirror-sg"
description = "Security group for PyPI mirror"
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] # Adjust this to your specific needs
}
ingress {
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] # Adjust this to your specific needs
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "pypi-mirror-sg"
}
}
Creating an EBS Volume
resource "aws_ebs_volume" "pypi_mirror_volume" {
availability_zone = aws_instance.pypi_mirror.availability_zone
size = 100 # Size in GB
type = "gp3" # Choose appropriate volume type
tags = {
Name = "pypi-mirror-volume"
}
}
Attaching the Volume to the Instance
resource "aws_ebs_volume_attachment" "pypi_mirror_attachment" {
volume_id = aws_ebs_volume.pypi_mirror_volume.id
device_name = "/dev/xvdf" # Adjust as needed based on your AMI
instance_id = aws_instance.pypi_mirror.id
}
Configuring the PyPI Mirror Software
Once the EC2 instance is running, you need to install and configure the PyPI mirror software. Bandersnatch is a popular choice. The exact steps will vary depending on your chosen software, but generally involve:
- Connect to the instance via SSH.
- Update the system packages. This ensures you have the latest versions of required utilities.
- Install Bandersnatch. This can typically be done via pip:
pip install bandersnatch. - Configure Bandersnatch. This involves creating a configuration file specifying the upstream PyPI URL, the local storage location, and other options. Refer to the Bandersnatch documentation for detailed instructions: https://bandersnatch.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
- Run Bandersnatch. Once configured, start the mirroring process. This may take a considerable amount of time, depending on the size of the PyPI index.
- Set up a web server (e.g., Nginx) to serve the mirrored packages.
Setting up a Load Balanced PyPI Mirror
For increased availability and resilience, consider using an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) in front of multiple EC2 instances. This setup distributes traffic across multiple PyPI mirror instances, ensuring high availability even if one instance fails.
You’ll need to extend your Terraform configuration to include:
- An AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Target group(s) to register your EC2 instances
- Listener(s) configured to handle HTTP and HTTPS traffic
This setup requires more complex Terraform configuration and careful consideration of security and network settings.
Maintaining Your PyPI Mirror
Regular maintenance is vital for a healthy PyPI mirror. This includes:
- Regular updates: Keep Bandersnatch and other software updated to benefit from bug fixes and performance improvements.
- Monitoring: Monitor the disk space usage, network traffic, and overall performance of your mirror. Set up alerts for critical issues.
- Regular synchronization: Regularly sync your mirror with the upstream PyPI to ensure you have the latest packages.
- Security: Regularly review and update the security group rules to prevent unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding setting up a PyPI mirror in AWS with Terraform:
Q1: What are the benefits of using a PyPI mirror?
A1: A PyPI mirror offers several advantages, including faster package downloads for developers within your organization, reduced load on the upstream PyPI server, and improved resilience against PyPI outages.
Q2: Can I use a different mirroring software instead of Bandersnatch?
A2: Yes, you can. Several other mirroring tools are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific requirements and preferences.
Q3: How do I scale my PyPI mirror to handle increased traffic?
A3: Scaling can be achieved by adding more EC2 instances to your load-balanced setup. Using an auto-scaling group allows for automated scaling based on predefined metrics.
Q4: How do I handle authentication if my organization uses private packages?
A4: Handling private packages requires additional configuration and might involve using authentication methods like API tokens or private registries which can be integrated with your PyPI mirror.
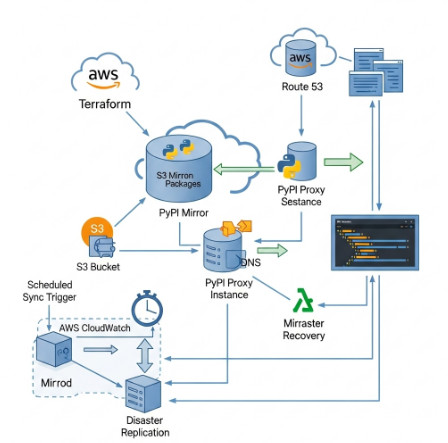
Conclusion
Setting up a PyPI mirror in AWS using Terraform provides a powerful and efficient solution for managing Python package dependencies. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a highly available and performant PyPI mirror, dramatically improving the speed and reliability of your Python development workflows. Remember to regularly monitor and maintain your mirror to ensure it remains efficient and secure. Choosing the right tools and strategies, including load balancing and auto-scaling, is key to building a robust and scalable solution for your organization’s needs. Thank you for reading the DevopsRoles page!

